Demystifying user journeys: Revolutionizing troubleshooting with auto tracking
Introduction
Troubleshooting critical issues by deciphering a user’s journey on the Grab app is an extremely challenging task. With countless user journeys and multiple paths through the User Interface (UI), it’s akin to searching for a needle in a vast haystack. This challenge frequently resonates with us, the dedicated developers at Grab, as we strive to understand user behaviors, views, and interactions.
The challenge
The distinction between resolving an issue effectively versus spending hours on a wild goose chase is understanding our user journey in real-time.
The development team initially attempted to address the issue of the incomplete user journey tracking by implementing a system where a click stream event would be sent with every user interaction. However, this approach presented significant challenges due to the sheer volume of UI components—often numbering in the hundreds—and the reliance on individual developers to correctly instrument each one.
A common pitfall was that developers would occasionally overlook or forget to instrument certain user interactions, leading to breaks in the recorded user journey. This created a highly frustrating situation for both the development and product teams, as the integrity of the user journey data was consistently compromised. Despite continuous efforts to patch these bugs and address the omissions, the team found themselves in a perpetual state of reaction, constantly trying to catch up with newly discovered breaches rather than proactively preventing them. This reactive approach consumed valuable resources and hindered the ability to gain a complete and accurate understanding of user behavior.
Diagnosing system failures, application bugs, or poor user experiences in complex applications becomes inefficient without real-time performance metrics and detailed session tracking. When engineering teams rely on outdated or fragmented data, they are forced to piece together issue narratives reactively, long after the issues occur. This significantly delays the Mean Time To Resolution (MTTR). Such a reactive approach leads to increased downtime, higher operational costs, customer dissatisfaction, and a waste of developers’ time, as they spend more time “hunting” for clues rather than deploying solutions or new features.
Our ‘Eureka’ moment: AutoTrack SDK
The pivotal breakthrough that provides our unique advantage was the creation of auto tracking user journeys—our “Eureka” moment. To deliver this, we developed the new Software Development Kit (SDK) called AutoTrack.
AutoTrack is system that comprehensively records application state, UI view state, as well as user interactions - a solution that pieces together a chronicle of the user journey, from launch to interactions, as they navigate through the screens. AutoTrack SDK is built on the three core pillars:
- Application state
- User interactions
- UI screens
Let’s delve deeper into the mechanics of how this operates.
Application state
Understanding the application state is fundamental to comprehending user behavior and, consequently, executing effective troubleshooting. The application state provides crucial insights into how a user interacts with the app, particularly concerning its visibility and how it was initiated. This encompasses tracking when the app moves between the background and foreground, as well as the various launch mechanisms.
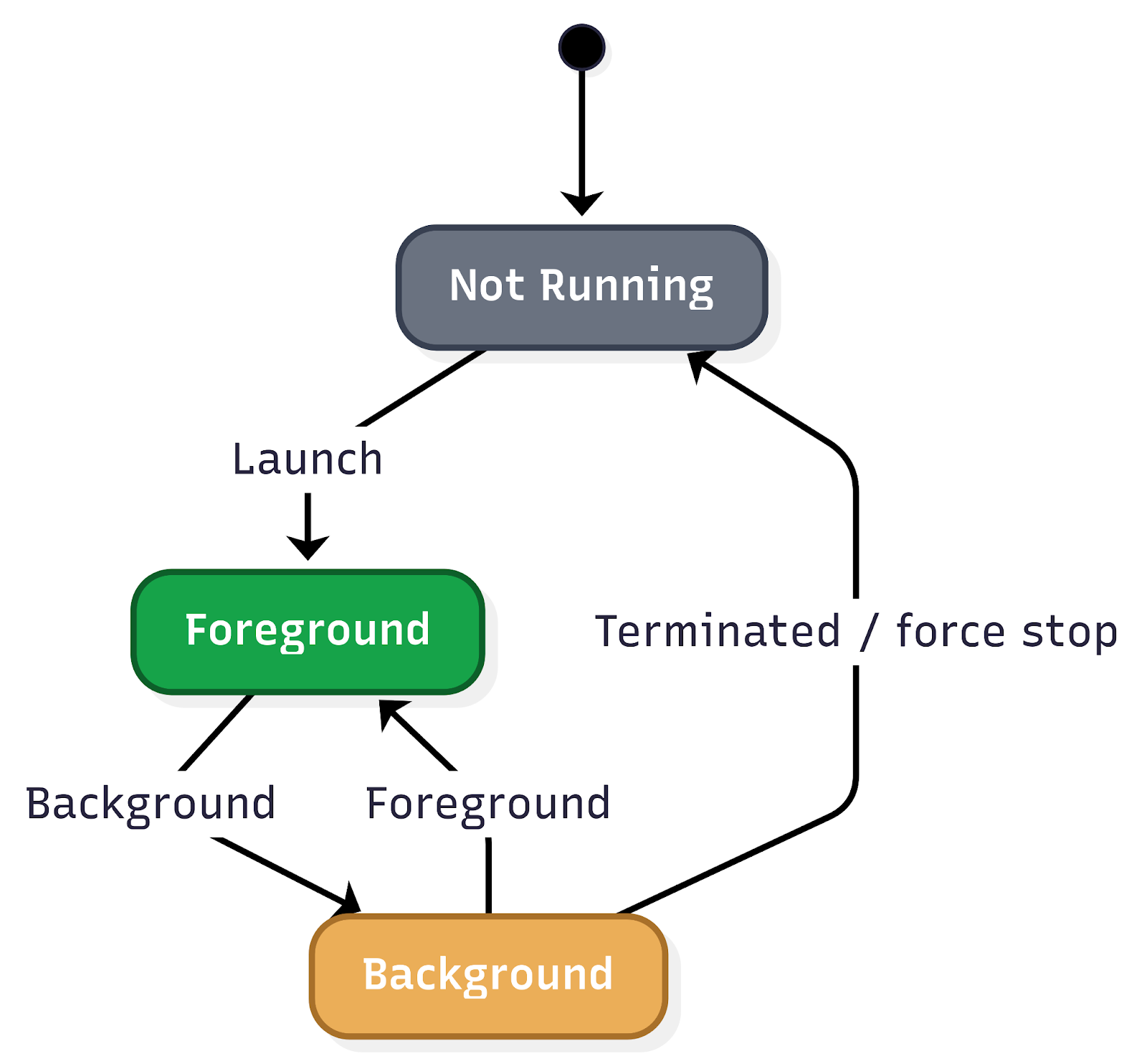
Key aspects of application state that are vital to monitor include:
Application lifecycle transitions:
- Background state: When the app is running but not actively displayed to the user (e.g., the user switches to another app, or the device is locked). Understanding how frequently and for how long an app resides in the background can inform power consumption analysis and the effectiveness of background tasks.
- Foreground state: When the app is actively in use and displayed to the user. Monitoring transitions into and out of the foreground provides a real-time view of user engagement.
- Inactive state: A temporary state where the app is in the foreground but not receiving events (e.g., an incoming call temporarily interrupts the app).
- Suspended state: An app that is in the background and has been explicitly suspended by the operating system to free up resources.
- Terminated state: When the app has been completely closed or crashed. Differentiating between intentional termination and crashes is critical for identifying stability issues.
Application launch mechanisms:
The way an app is launched significantly impacts the initial user experience and can influence subsequent interactions. Tracking these different launch types is essential for understanding user entry points and for debugging issues that might be specific to a particular launch method.
- Explicit user launch: This is the most straightforward launch mechanism, where the user directly taps on the app icon from their device’s home screen or app drawer. This indicates a deliberate intent to use the app and often signifies a primary entry point for regular users.
- Deeplinks: Deeplinks are URLs that, when clicked, open a specific page or section within a mobile app rather than a web page. They are powerful tools for enhancing user experience and engagement by providing direct access to relevant content.
- Push notifications: Push notifications are messages sent by an app to a user’s device even when the app is not actively in use. Tapping on a push notification often launches the app and directs the user to a specific context related to the notification’s content.

User interactions
Real-time session tracking is a crucial component in understanding user behavior and optimizing app performance. By meticulously tracking a wide array of user interactions, the system provides invaluable insights into how users navigate and engage with the app. This granular data forms the bedrock for constructing comprehensive user journeys, allowing development teams to visualise the path a user takes from their initial entry point to achieving their goals within the app.
This deep understanding of user interactions is the most important pillar in creating accurate and insightful user journey maps. These maps, in turn, are instrumental in identifying patterns of user behavior, both positive and negative. For instance, tracking helps to identify pain points, bugs, or areas of confusion that might lead to user frustration or abandonment.

UI screen
The system leverages lifecycle events from UIViewController (iOS), Activity (Android), and Fragments (Android) to accurately identify and track which specific screen is currently displayed to the user. This granular level of screen tracking is crucial because it significantly enriches the contextual information available to us. By understanding the precise UI that users are interacting with, we can account for the dynamic nature of our app. Different geographical regions, diverse user segments, and varying operational scenarios can lead to distinct user interfaces being presented. This capability ensures that our analysis and troubleshooting efforts are always based on the actual user experience, allowing for more precise problem identification and more effective solutions.

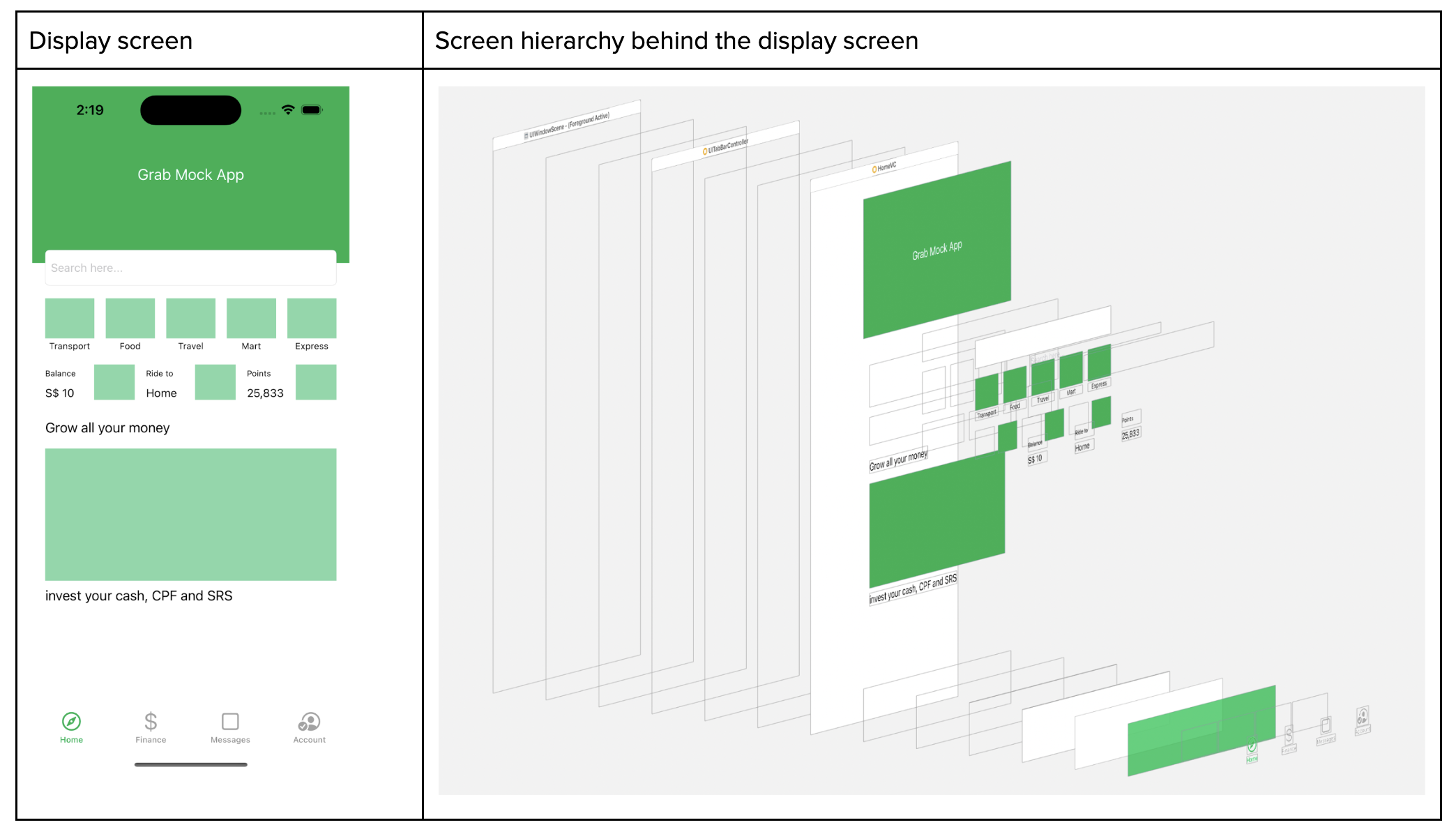
UI screen data
On top of that, whenever the screen appears, we capture the screen metadata where we read the full screen hierarchy. With the Screen hierarchy JSON data at hand, we employ it to train an AI model. This model, consequently, can generate an HTML file, which mirrors the user’s screen and interaction.
Disclaimer: information is redacted in compliance with GDPR/PDPA, personal data protection laws.
Applications of AutoTrack
Key applications of AutoTrack data:
- Reconstructing user journeys and reproducing elusive bugs: One of the most significant benefits of AutoTrack is its ability to meticulously record user interactions within the app. This detailed session data allows our teams to precisely recreate the user journey that led to a reported issue. For bugs that are notoriously difficult to reproduce, this capability is a game-changer, eliminating hours of manual guesswork and dramatically accelerating the identification and resolution of underlying problems.
- Automated issue assignment: When an issue is reported, AutoTrack data can be leveraged to automatically assign it to the most relevant team. By analysing the context of the issue within the recorded session, including the specific features or modules involved, the system can intelligently route the problem to the engineers best equipped to address it. This automation reduces triage time, ensures issues are handled by subject matter experts, and improves overall response efficiency.
- Automating UI test case generation: The rich dataset provided by AutoTrack offers a powerful foundation for automating the creation of UI test cases. By observing how users interact with the interface, we can automatically generate test scripts that mimic real-world usage patterns. This not only speeds up the testing phase but also leads to more comprehensive test coverage, identifying edge cases and user flows that might otherwise be missed by manually written tests.
- Understanding analytics event triggers: AutoTrack data provides a granular view into when and why specific analytics events are triggered within the application. This allows us to validate the accuracy of our analytics instrumentation, ensure that events are firing as expected, and gain deeper insights into user behavior. By understanding the precise context surrounding event triggers, we can refine our data collection strategies and derive more meaningful insights from our analytics.
Key takeaways and what’s next
AutoTrack replaces fragile manual instrumentation with a unified, real-time view of application state, screen context, and user interactions. That end-to-end trace makes elusive bugs reproducible, routes issues to the right owners, and seeds reliable UI tests—turning guesswork into grounded evidence so teams can ship fixes faster and with greater confidence.
Looking ahead, we are expanding AutoTrack across surfaces and deepening the context it captures—pairing sessions with network and performance signals, strengthening privacy guardrails, and integrating with automated triage and test generation. Look forward to reading more of our deep dives on auto-generated UI tests and how these journeys will power proactive quality across Grab’s app.
Join us
Grab is a leading superapp in Southeast Asia, operating across the deliveries, mobility and digital financial services sectors. Serving over 800 cities in eight Southeast Asian countries, Grab enables millions of people everyday to order food or groceries, send packages, hail a ride or taxi, pay for online purchases or access services such as lending and insurance, all through a single app. Grab was founded in 2012 with the mission to drive Southeast Asia forward by creating economic empowerment for everyone. Grab strives to serve a triple bottom line – we aim to simultaneously deliver financial performance for our shareholders and have a positive social impact, which includes economic empowerment for millions of people in the region, while mitigating our environmental footprint.
Powered by technology and driven by heart, our mission is to drive Southeast Asia forward by creating economic empowerment for everyone. If this mission speaks to you, join our team today!


