 Engineering
·
Security
Engineering
·
Security
Graph modelling guidelines
Introduction
Graph modelling is a highly effective technique for representing and analysing complex and interconnected data across various domains. By deciphering relationships between entities, graph modelling can reveal insights that might be otherwise difficult to identify using traditional data modelling approaches. In this article, we will explore what graph modelling is and guide you through a step-by-step process of implementing graph modelling to create a social network graph.
What is graph modelling?
Graph modelling is a method for representing real-world entities and their relationships using nodes, edges, and properties. It employs graph theory, a branch of mathematics that studies graphs, to visualise and analyse the structure and patterns within complex datasets. Common applications of graph modelling include social network analysis, recommendation systems, and biological networks.
Graph modelling process
Step 1: Define your domain
Before diving into graph modelling, it’s crucial to have a clear understanding of the domain you’re working with. This involves getting acquainted with the relevant terms, concepts, and relationships that exist in your specific field. To create a social network graph, familiarise yourself with terms like users, friendships, posts, likes, and comments.
Step 2: Identify entities and relationships
After defining your domain, you need to determine the entities (nodes) and relationships (edges) that exist within it. Entities are the primary objects in your domain, while relationships represent how these entities interact with each other. In a social network graph, users are entities, and friendships are relationships.
Step 3: Establish properties
Each entity and relationship may have a set of properties that provide additional information. In this step, identify relevant properties based on their significance to the domain. A user entity might have properties like name, age, and location. A friendship relationship could have a ‘since’ property to denote the establishment of the friendship.
Step 4: Choose a graph model
Once you’ve identified the entities, relationships, and properties, it’s time to choose a suitable graph model. Two common models are:
- Property graph: A versatile model that easily accommodates properties on both nodes and edges. It’s well-suited for most applications.
- Resource Description Framework (RDF): A World Wide Web Consortium (W3C) standard model, using triples of subject-predicate-object to represent data. It is commonly used in semantic web applications.
For a social network graph, a property graph model is typically suitable. This is because user entities have many attributes and features. Property graphs provide a clear representation of the relationships between people and their attribute profiles.
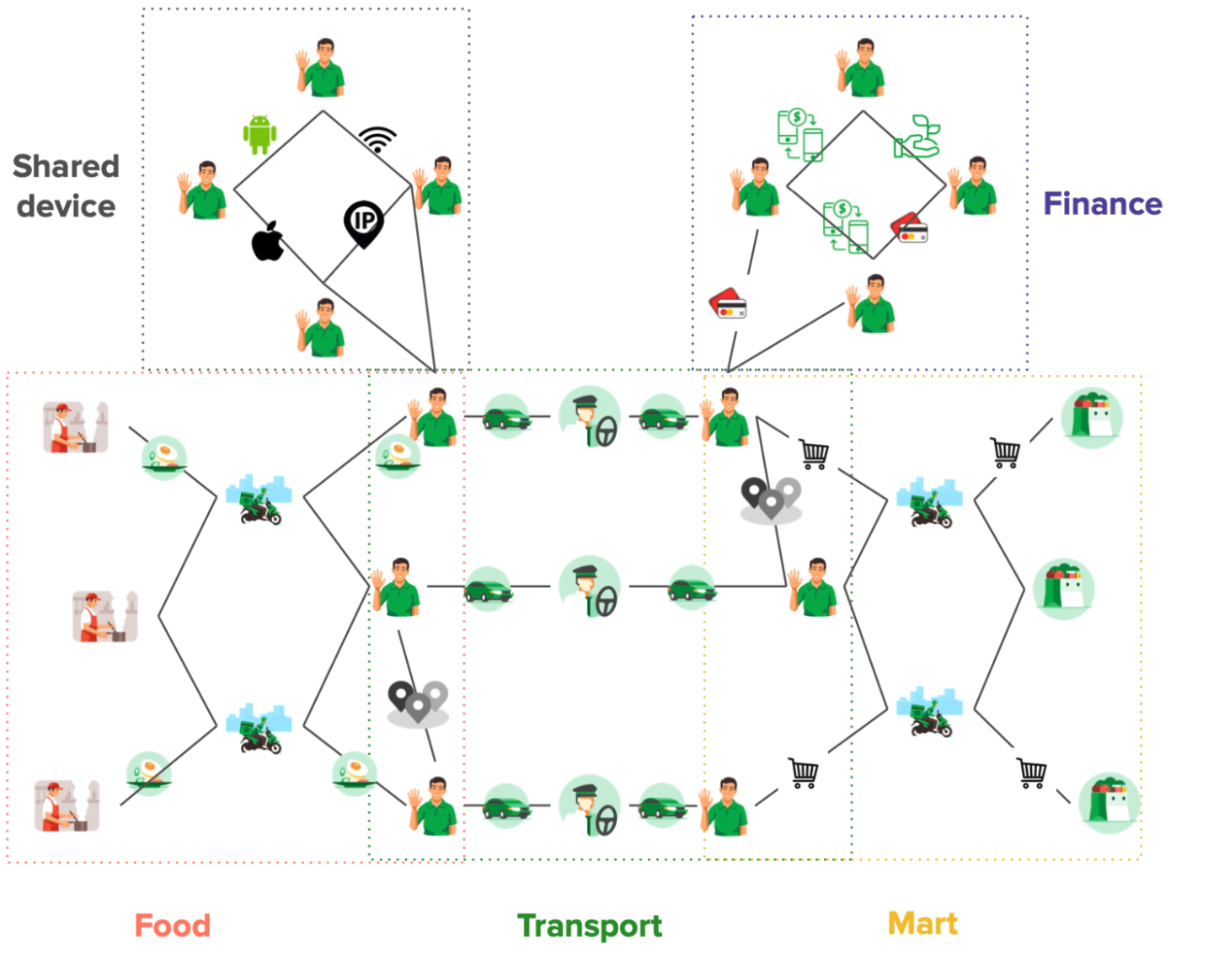
Step 5: Develop a schema
Although not required, developing a schema can be helpful for large-scale projects and team collaborations. A schema defines the structure of your graph, including entity types, relationships, and properties. In a social network graph, you might have a schema that specifies the types of nodes (users, posts) and the relationships between them (friendships, likes, comments).
Step 6: Import or generate data
Next, acquire the data needed to populate your graph. This can come in the form of existing datasets or generated data from your application. For a social network graph, you can import user information from a CSV file and generate simulated friendships, posts, likes, and comments.
Step 7: Implement the graph using a graph database or other storage options
Finally, you need to store your graph data using a suitable graph database. Neo4j, Amazon Neptune, or Microsoft Azure Cosmos DB are examples of graph databases. Alternatively, depending on your specific requirements, you can use a non-graph database or an in-memory data structure to store the graph.
Step 8: Analyse and visualise the graph
After implementing the graph, you can perform various analyses using graph algorithms, such as shortest path, centrality, or community detection. In addition, visualising your graph can help you gain insights and facilitate communication with others.
Conclusion
By following these steps, you can effectively create and analyse graph models for your specific domain. Remember to adjust the steps according to your unique domain and requirements, and always ensure that confidential and sensitive data is properly protected.
References
Join us
Grab is the leading superapp platform in Southeast Asia, providing everyday services that matter to consumers. More than just a ride-hailing and food delivery app, Grab offers a wide range of on-demand services in the region, including mobility, food, package and grocery delivery services, mobile payments, and financial services across 428 cities in eight countries.
Powered by technology and driven by heart, our mission is to drive Southeast Asia forward by creating economic empowerment for everyone. If this mission speaks to you, join our team today!



