 Engineering
·
Data Science
Engineering
·
Data Science
Supercharging LLM application development with LLM-Kit
Introduction
At Grab, we are committed to leveraging the power of technology to deliver the best services to our users and partners. As part of this commitment, we have developed the LLM-Kit, a comprehensive framework designed to supercharge the setup of production-ready Generative AI applications. This blog post will delve into the features of the LLM-Kit, the problems it solves, and the value it brings to our organisation.
Challenges
The introduction of the LLM-Kit has significantly addressed the challenges encountered in LLM application development. The involvement of sensitive data in AI applications necessitates that security remains a top priority, ensuring data safety is not compromised during AI application development.
Concerns such as scalability, integration, monitoring, and standardisation are common issues that any organisation will face in their LLM and AI development efforts.
The LLM-Kit has empowered Grab to pursue LLM application development and the rollout of Generative AI efficiently and effectively in the long term.
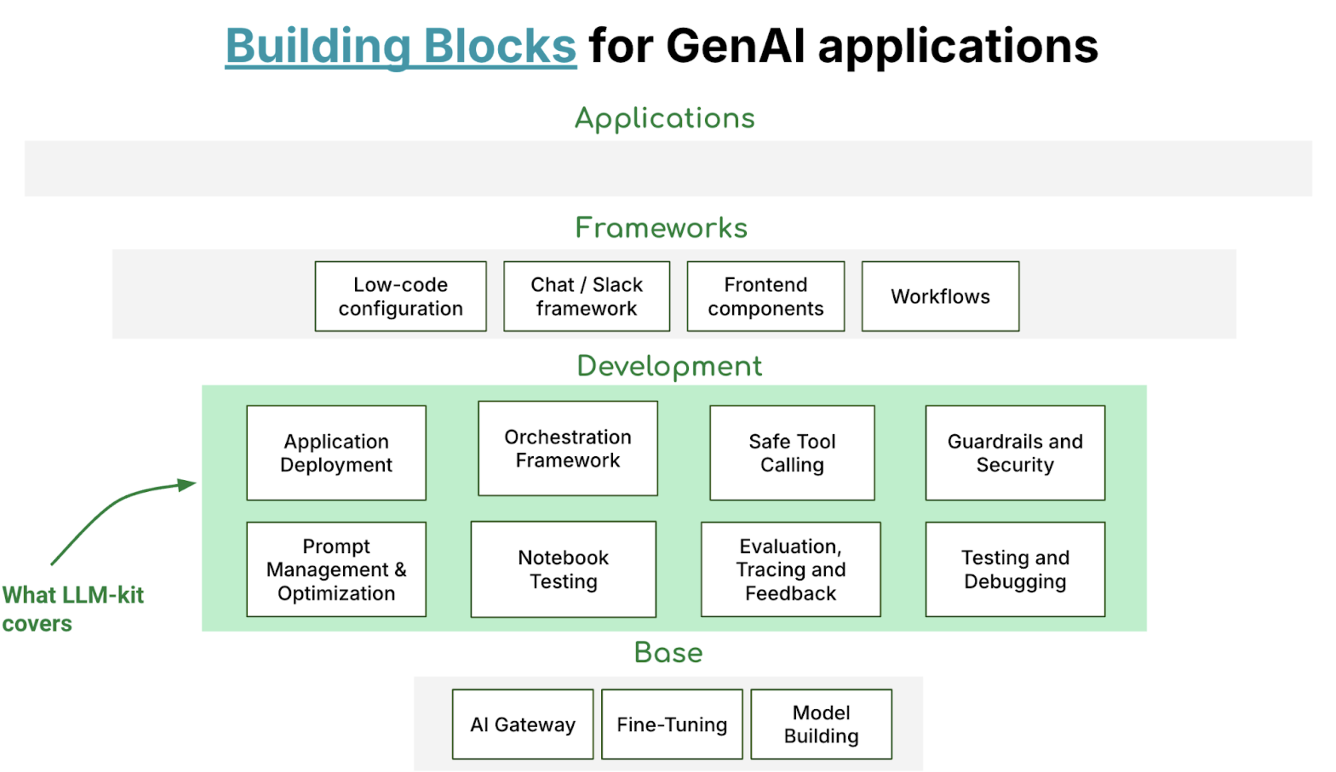
Introducing the LLM-Kit
The LLM-Kit is our solution to these challenges. Since the introduction of the LLM Kit, it has helped onboard hundreds of GenAI applications at Grab and has become the de facto choice for developers. It is a comprehensive framework designed to supercharge the setup of production-ready LLM applications. The LLM-Kit provides:
- Pre-configured structure: The LLM-Kit comes with a pre-configured structure containing an API server, configuration management, a sample LLM Agent, and tests.
- Integrated tech stack: The LLM-Kit integrates with Poetry, Gunicorn, FastAPI, LangChain, LangSmith, Hashicorp Vault, Amazon EKS, and Gitlab CI pipelines to provide a robust and end-to-end tech stack for LLM application development.
- Observability: The LLM-Kit features built-in observability with Datadog integration and LangSmith, enabling real-time monitoring of LLM applications.
- Config & secret management: The LLM-Kit utilises Python’s configparser and Vault for efficient configuration and secret management.
- Authentication: The LLM-Kit provides built-in OpenID Connect (OIDC) auth helpers for authentication to Grab’s internal services.
- API documentation: The LLM-Kit features comprehensive API documentation using Swagger and Redoc.
- Redis & vector databases integration: The LLM-Kit integrates with Redis and Vector databases for efficient data storage and retrieval.
- Deployment pipeline: The LLM-Kit provides a deployment pipeline for staging and production environments.
- Evaluations: The LLM-Kit seamlessly integrates with LangSmith, utilising its robust evaluations framework to ensure the quality and performance of the LLM applications.
In addition to these features, the team has also included a cookbook with many commonly used examples within the organisation providing a valuable resource for developers. Our cookbook includes a diverse range of examples, such as persistent memory agents, Slackbot LLM agents, image analysers and full-stack chatbots with user interfaces, showcasing the versatility of the LLM-Kit.
The value of the LLM-Kit
The LLM-Kit brings significant value to our teams at Grab:
- Increased development velocity: By providing a pre-configured structure and integrated tech stack, the LLM-Kit accelerates the development of LLM applications.
- Improved observability: With built-in LangSmith and Datadog integration, teams can monitor their LLM applications in real-time, enabling faster issue detection and resolution.
- Enhanced security: The LLM-Kit’s built-in OIDC auth helpers and secret management using Vault ensure the secure development and deployment of LLM applications.
- Efficient data management: The integration with Vector databases facilitates efficient data storage and retrieval, crucial for the performance of LLM applications.
- Standardisation: The LLM-Kit provides a paved-road framework for building LLM applications, promoting best practices and standardisation across teams.
Through the LLM-Kit, we can save an estimate of 1.5 weeks before teams start working on their first feature.
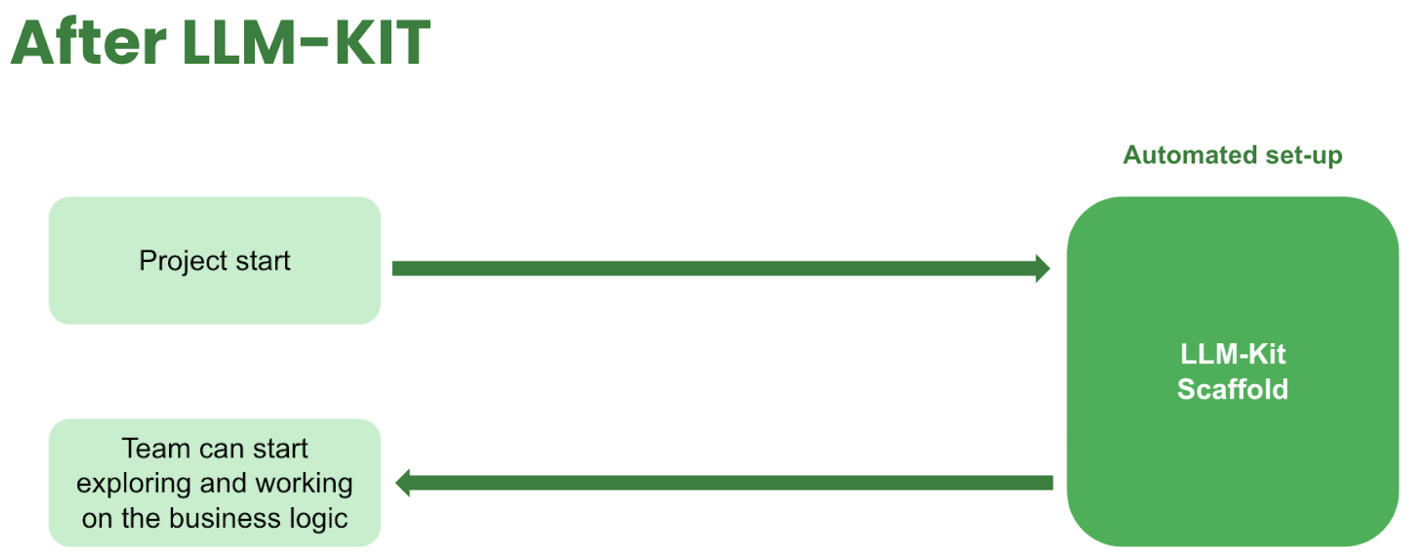
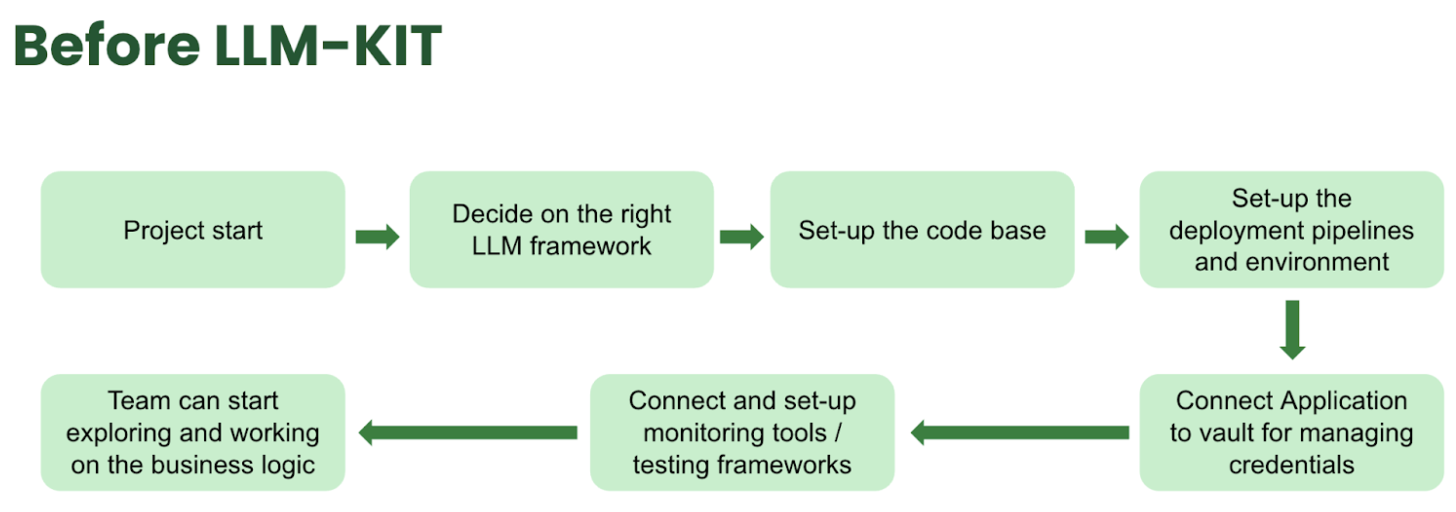

Architecture design and technical implementation
The LLM-Kit is designed with a modular architecture that promotes scalability, flexibility, and ease of use.
Automated steps
To better illustrate the technical implementation of the LLM-Kit, let’s take a look at figure 4 which outlines the step-by-step process of how an LLM application is generated with the LLM-Kit:
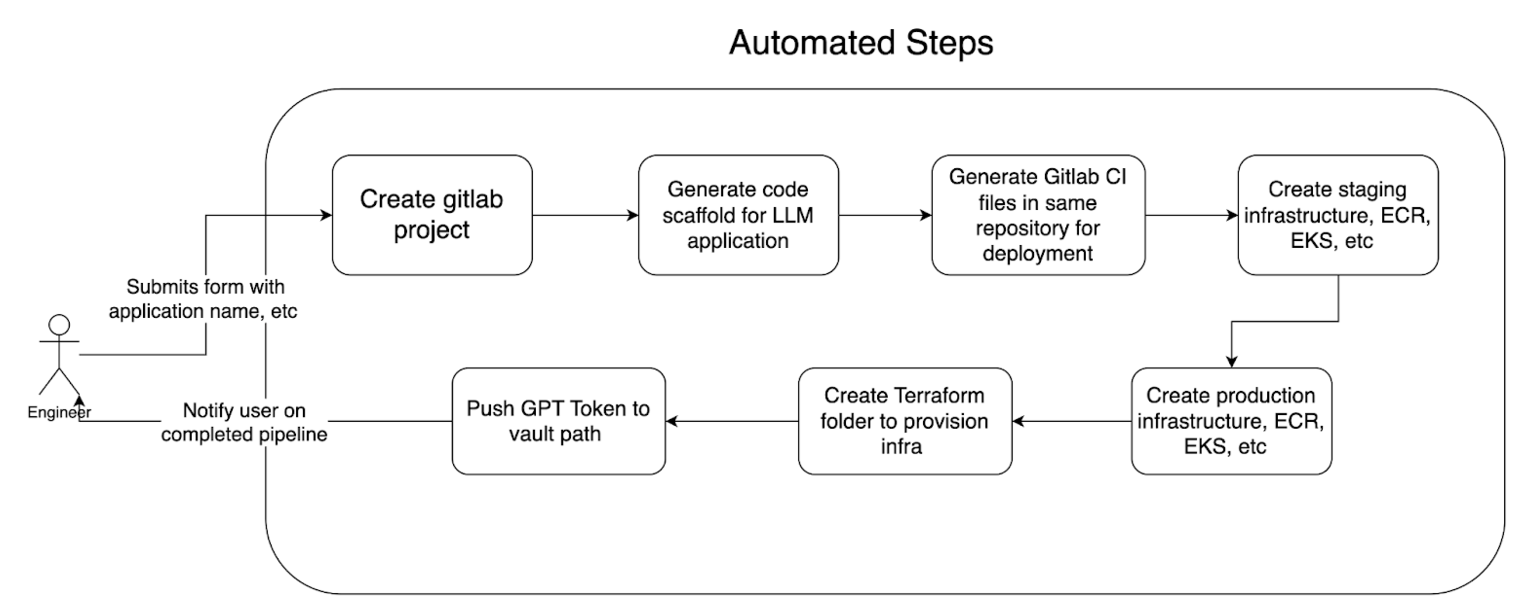
The process begins when an engineer submits a form with the application name and other relevant details. This triggers the creation of a GitLab project, followed by the generation of a code scaffold specifically designed for the LLM application. GitLab CI files are then generated within the same repository to handle continuous integration and deployment tasks. The process continues with the creation of staging infrastructure, including components like Elastic Container Registry (ECR) and Elastic Kubernetes Service (EKS). Additionally, a Terraform folder is created to provision the necessary infrastructure, eventually leading to the deployment of production infrastructure. At the end of the pipeline, a GPT token is pushed to a secure Vault path, and the engineer is notified upon the successful completion of the pipeline.
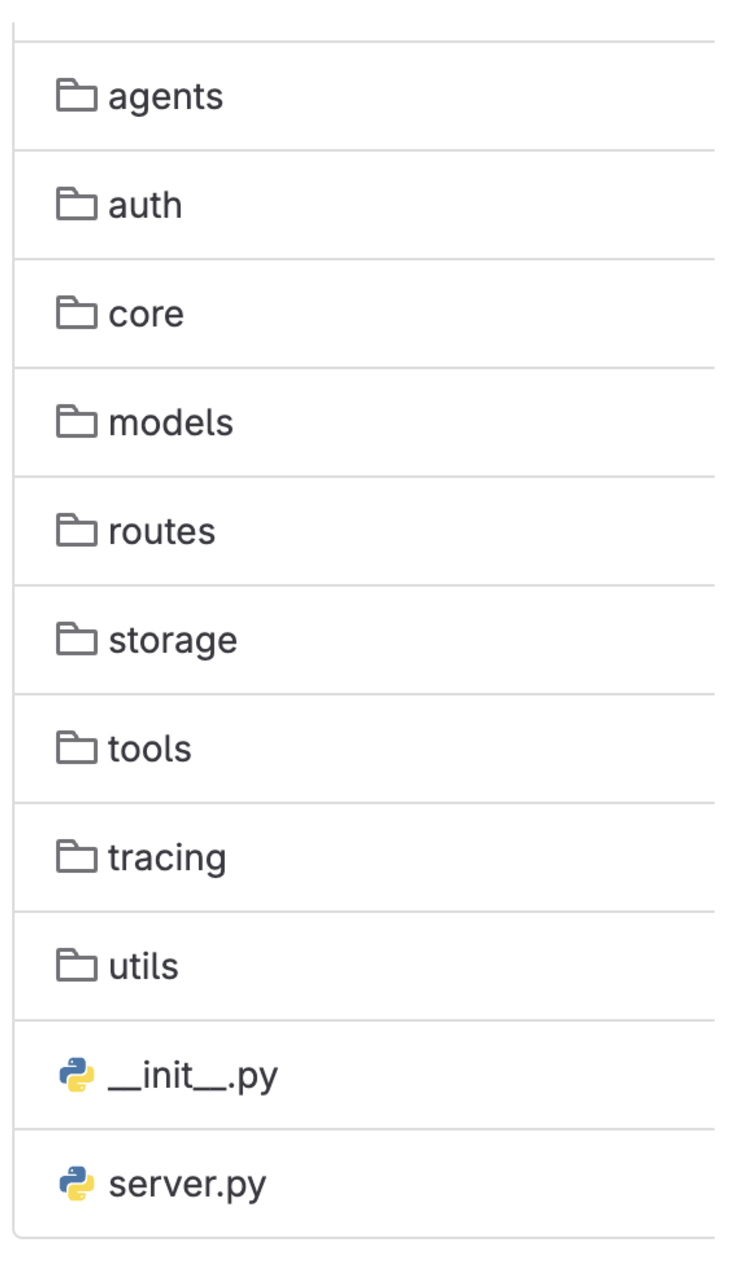
Scaffold code structure
The scaffolded code is broken down into multiple folders:
- Agents: Contains the code to initialise an agent. We have gone ahead with LangChain as the agent framework; essentially the entry point for the endpoint defined in the Routes folder.
- Auth: Authentication and authorisation module for executing some of the APIs within Grab.
- Core: Includes extracting all configurations (i.e. GPT token) and secret decryption for running the LLM application.
- Models: Used to define the structure for the core LLM APIs within Grab.
- Routes: REST API endpoint definitions for the LLM Applications. It comes with health check, authentication, authorisation, and a simple agent by default.
- Storage: Includes connectivity with PGVector, our managed vector database within Grab and database schemas.
- Tools: Functions which are used as tools for the LLM Agent.
- Tracing: Integration with our tracing and monitoring tools to monitor various metrics for a production application.
- Utils: Default folder for utility functions.
Infrastructure provisioning and deployment
Within the same codebase, we have integrated a comprehensive pipeline that automatically scaffolds the necessary code for infrastructure provisioning, deployment, and build processes. Using Terraform, the pipeline provisions the required infrastructure seamlessly. The deployment pipelines are defined in the .gitlab-ci.yml file, ensuring smooth and automated deployments. Additionally, the build process is specified in the Dockerfile, allowing for consistent builds. This automated scaffolding streamlines the development workflow, enabling developers to focus on writing business logic without worrying about the underlying infrastructure and deployment complexities.
RAG scaffolding
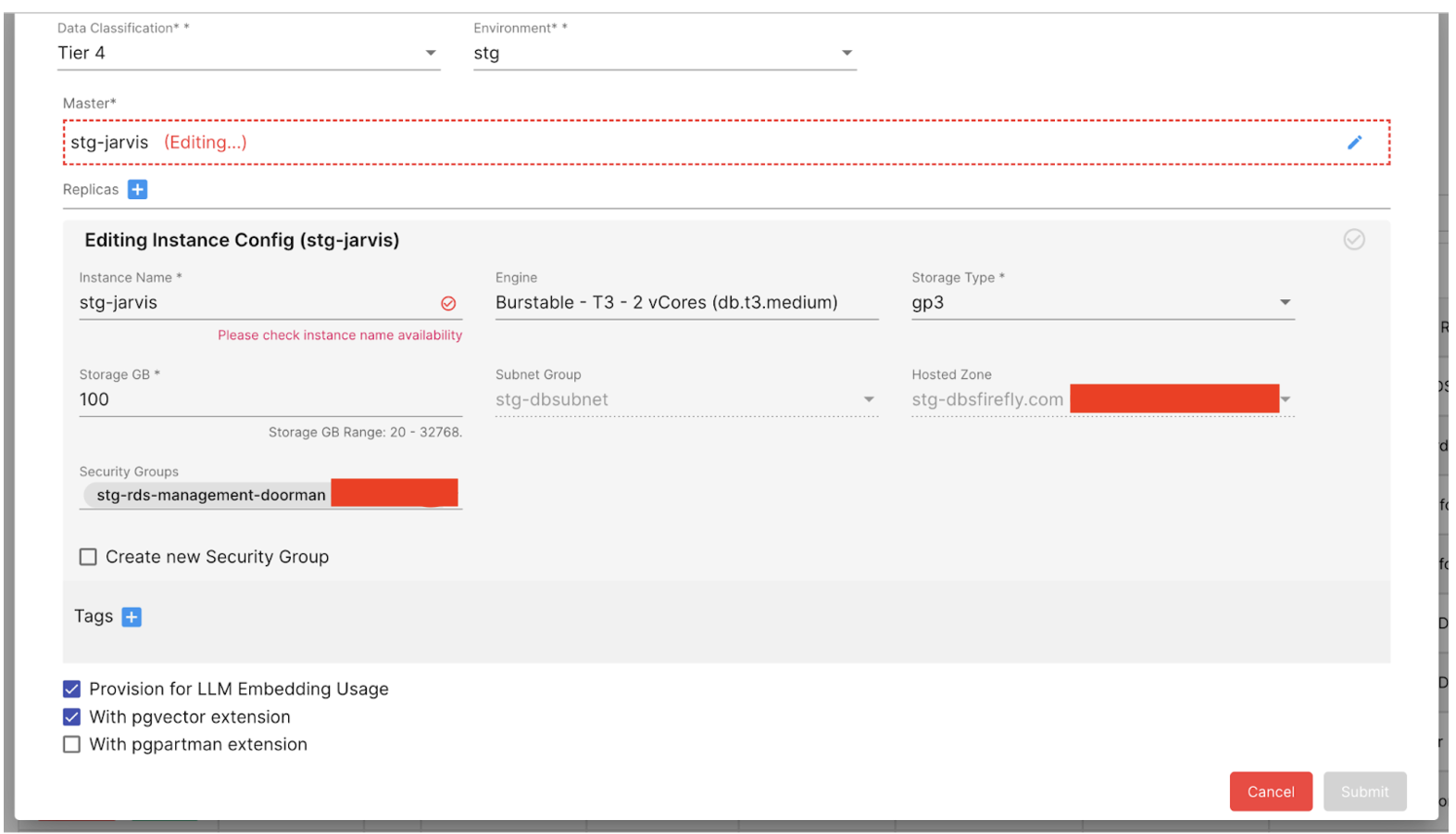
At Grab, we’ve established a streamlined process for setting up a vector database (PGVector) and whitelisting the service using the LLM-Kit. Once the form (figure 7) is submitted, you can access the credentials and database host path. The secrets will be automatically added to the Vault path. Engineers will then only need to include the DB host path in the configuration file of the scaffolded LLM-Kit application.
Conclusion
The LLM-Kit is a testament to Grab’s commitment to fostering innovation and growth in AI and ML. By addressing the challenges faced by our teams and providing a comprehensive, scalable, and flexible framework for LLM application development, the LLM-Kit is paving the way for the next generation of AI applications at Grab.
Growth and future plans
Looking ahead, the LLM-Kit team aims to significantly enhance the web server’s concurrency and scalability while providing reliable and easy-to-use SDKs. The team plans to offer reusable and composable LLM SDKs, including evaluation and guardrails frameworks, to enable service owners to build feature-rich Generative AI programs with ease. Key initiatives also include the development of a CLI for version updates and dev tooling, as well as a polling-based agent serving function. These advancements are designed to drive innovation and efficiency within the organisation, ultimately providing a more seamless and efficient development experience for engineers.
We would like to acknowledge and thank Pak Zan Tan, Han Su, and Jonathan Ku from the Yoshi team and Chen Fei Lee from the MEKS team for their contribution to this project under the leadership of Padarn George Wilson.
Join us
Grab is the leading superapp platform in Southeast Asia, providing everyday services that matter to consumers. More than just a ride-hailing and food delivery app, Grab offers a wide range of on-demand services in the region, including mobility, food, package and grocery delivery services, mobile payments, and financial services across 700 cities in eight countries.
Powered by technology and driven by heart, our mission is to drive Southeast Asia forward by creating economic empowerment for everyone. If this mission speaks to you, join our team today!



