 Engineering
Engineering
DispatchGym: Grab’s reinforcement learning research framework
Introduction
DispatchGym is a research framework designed to facilitate Reinforcement Learning (RL) studies and applications for the dispatch system, which matches bookings with drivers. The primary goal is to empower data scientists with a tool that allows them to independently develop and test RL-related concepts for dispatching systems. It accelerates research by providing a suite of modules that include a reinforcement learning algorithm, a dispatching process simulation, and an interface connecting the two through the Gymnasium API.
To ensure efficient and cost-effective RL research without compromising on quality, DispatchGym aims to be both comprehensive and accessible. Anyone with basic RL knowledge and Python programming skills can use it to explore new ideas in RL and dispatch system logic.
This article walks you through the principles behind DispatchGym, how these principles effectively and efficiently empower impactful research, and how it can be applied to solve real world problems.
The challenge with RL
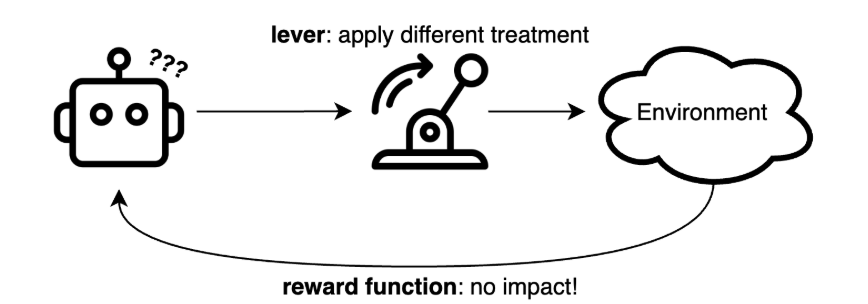
Although RL methods can be applied to a wide variety of problems that can be formulated as a Markov Decision Process (MDP), designing an effective RL-based solution is not a trivial task. The primary challenges stem from two key components: the reward function and the lever.
In RL, the reward function represents the objective we aim to maximize. At first glance, it might seem straightforward to plug in any metric, such as the company’s profit or the number of completed bookings per day. However, these metrics are not always sensitive to the lever that RL can manipulate, or the lever itself may not significantly influence the objective. For example, consider a setup where we aim to maximize the daily number of completed bookings by adjusting the maximum number of candidate drivers considered to each booking. Beyond a minimal threshold (e.g., one driver), further increasing this limit provides negligible benefits. As a result, RL struggles to determine whether setting this limit to 11 or 15 would result in higher rewards.
In summary, when a lever exerts weak influence on a reward function, the RL setup becomes ineffective. Therefore, we should strive to select a lever that strongly influences the reward function and define a reward function that is both sensitive to manipulations of that lever and aligned with our overall goal. Note that the reward function does not have to be identical to our ultimate objective; it merely needs to be highly correlated with it.
Empowering research with DispatchGym
The primary application of DispatchGym is to accelerate and broaden cost-effective research and impactful RL applications for Grab’s dispatching system. A system which is responsible for assigning a driver to each booking. To achieve this, DispatchGym must have the following characteristics:
-
Reliable
The simulation component should be accurate enough to capture essential behaviors strongly linked to the metrics of interest, without necessarily modeling everything else. While it’s beneficial if the simulation can do more than the specific use case (e.g., simulating both batching and allocation when only allocation is needed), it is not strictly required. -
Cost-effective
Updating all of DispatchGym’s components should require minimal monetary and labor costs to enable rapid iteration. This includes keeping the simulation component aligned with real system behaviors, incorporating the latest technologies in the optimization component, and maintaining seamless integration between the simulation and optimization components. -
Empowering
It should be as easy as possible for data scientists and engineers to modify any DispatchGym component and then run experiments. This flexibility is crucial because new research typically requires adjustments to both the simulation and optimization components. By granting users the freedom to adapt DispatchGym, the framework fosters continuous innovation.
Research-friendly simulated environment
The simulation component of DispatchGym, or the “simulated environment,” is designed with reliability, cost-effectiveness, and user empowerment in mind. It models the full dispatching process, from booking creation and driver dispatch to driver movement and booking completion. While this environment may not be perfectly accurate in absolute terms (there can be differences between real and simulated metric values), it emphasizes directional accuracy. This means that the metric trends (up or down) in the simulation closely match real-world behavior. This focus on directional accuracy is crucial because most research involves sim-to-sim comparisons, where shifts in metrics are the most important. Verifying directional accuracy is also simpler and more practical for evaluating simulation performance. For instance, we can test various supply-demand imbalance scenarios and check whether a supply-rich situation indeed fulfills more bookings, and vice versa.
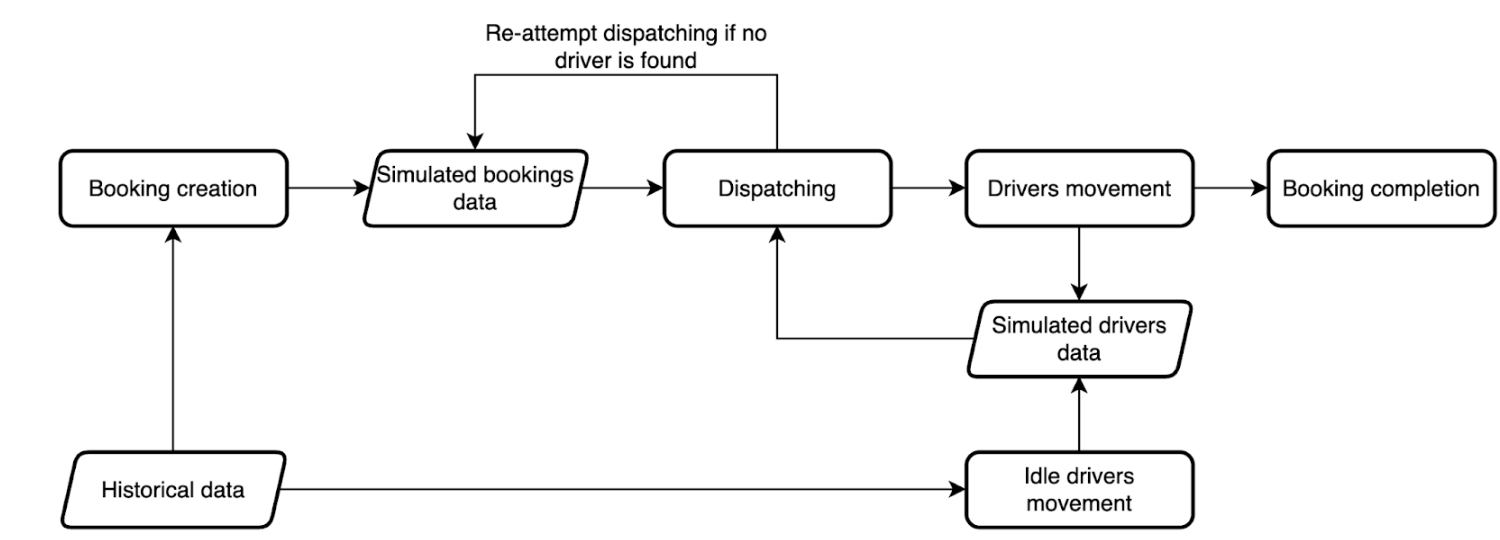
The simulated environment’s cost-effectiveness and empowerment features come from a modular architecture and Python, a research-friendly programming language. The modular design offers a gentle learning curve, allowing users to easily navigate and make necessary changes in the codebase. Meanwhile, Python is selected to lower the entry barrier for adopting DispatchGym. To mitigate Python’s runtime overhead, DispatchGym leverages Numba to significantly speed up simulation execution.
DispatchGym in action
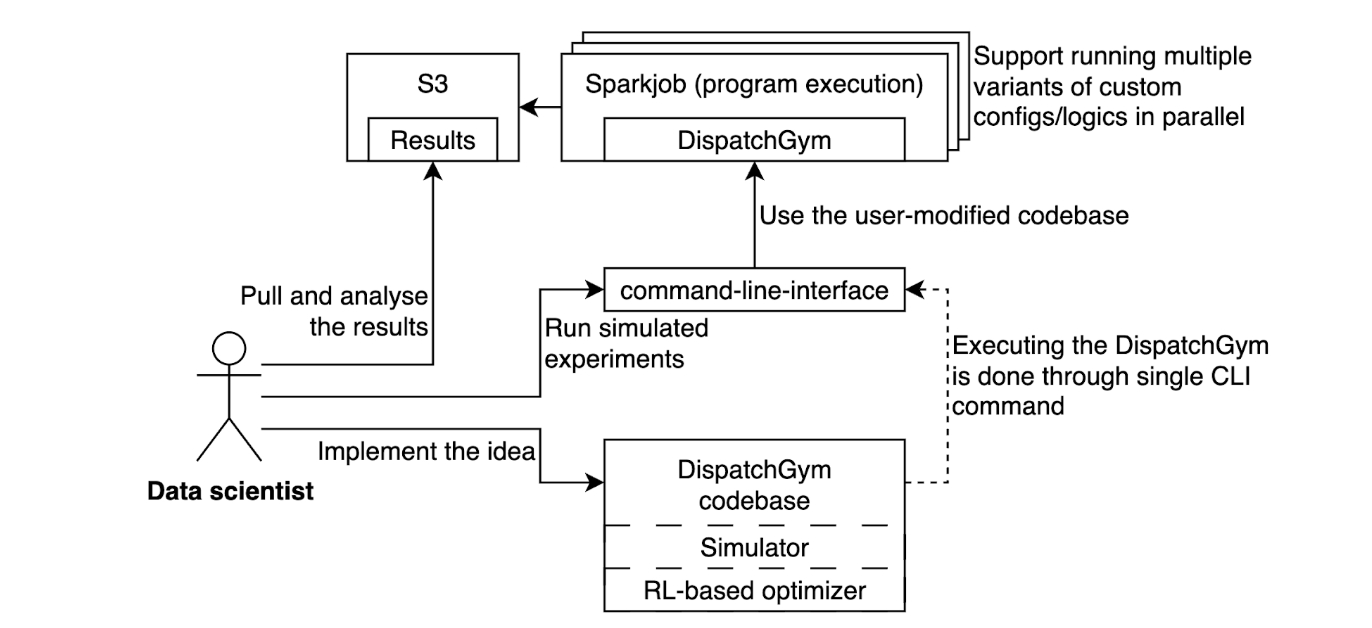
Data scientists use DispatchGym by modifying a local copy of the codebase to implement their ideas. They then upload the updated codebase to an internal infrastructure using a single CLI command, which spawns a Spark job to run the DispatchGym program. This setup grants complete flexibility over the simulation and optimization components without requiring users to manage the underlying infrastructure.
Applying RL approach for dispatch
Amongst its many uses, DispatchGym was applied in building an effective contextual bandit strategy for the auto-adaptive tuning of dispatch-related hyperparameters. Its flexibility allowed us to experiment with various contextual bandit model variants, including linear bandits, neural-linear bandits, and Gaussian-process bandits, as well as multiple action sampling strategies, such as epsilon-greedy, Thompson sampling, SquareCB, and FastCB. These capabilities accelerated our progress in determining the best combination of levers, reward functions, and contextual bandits for improved fulfilment efficiency and reliability.
Conclusion
DispatchGym provides us a framework that equips data scientists with everything they need to develop and test RL solutions for dispatch systems. By integrating an RL optimization approach and a realistic dispatch simulation using a Gymnasium API, it enables rapid exploration and iteration of RL applications with just basic RL knowledge and Python programming language.
A major hurdle in applying RL to dispatch problems modeled as MDP is ensuring that the reward function aligns with ultimate business goals and is sensitive to the lever under control. If the lever (e.g., tweaking driver count) does not meaningfully influence the reward, the RL approach falters. DispatchGym addresses this by making it easy for data scientists to determine the most effective combinations of levers, reward functions, and RL approaches, ultimately driving positive business impact.
DispatchGym’s architecture focuses on reliability, cost-effectiveness, and user empowerment. Its simulation is designed to capture critical metrics and reflect real-world trends (directional accuracy), while its Python-based modular design enhanced by Numba enables easy prototyping. Researchers can adjust the environment locally before deploying changes seamlessly via a command-line interface, avoiding infrastructure overhead. These design decisions and capabilities empower data scientists to refine contextual bandit approaches for optimizing dispatch hyperparameters and explore innovative RL applications in the dispatch process.
We would like to thank Chongyu Zhou, Guowei Wong, and Roman Kotelnikov for their collaboration in developing the RL-based optimizer.
Join us
Grab is a leading superapp in Southeast Asia, operating across the deliveries, mobility and digital financial services sectors. Serving over 800 cities in eight Southeast Asian countries, Grab enables millions of people everyday to order food or groceries, send packages, hail a ride or taxi, pay for online purchases or access services such as lending and insurance, all through a single app. Grab was founded in 2012 with the mission to drive Southeast Asia forward by creating economic empowerment for everyone. Grab strives to serve a triple bottom line – we aim to simultaneously deliver financial performance for our shareholders and have a positive social impact, which includes economic empowerment for millions of people in the region, while mitigating our environmental footprint.
Powered by technology and driven by heart, our mission is to drive Southeast Asia forward by creating economic empowerment for everyone. If this mission speaks to you, join our team today!


