Engineering
·
Data
Engineering
·
Data
SpellVault’s evolution: Beyond LLM apps, towards the agentic future
Introduction
At Grab, innovation isn’t just about building new features; it’s about evolving our platforms to meet the changing needs of our users and the broader technological landscape. SpellVault, our internal AI platform, exemplifies this philosophy. When SpellVault was first launched, our vision was straightforward: empower everyone at Grab to effortlessly build and manage AI-powered apps without the need for coding. Built on the principles of Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) and enhanced by plugin support, SpellVault rapidly evolved into a powerful productivity engine for the organization, enabling the creation of thousands of apps that drive automation, foster experimentation, and support production use cases.
As the AI landscape has evolved, SpellVault has grown alongside it. Initially launched as a straightforward no-code app builder for Large Language Models (LLMs), it has now evolved into a cutting-edge platform that embraces the agentic future—a future where AI goes beyond generating responses to reasoning, acting, and dynamically adapting through the use of tools and contextual understanding.
This article outlines SpellVault’s journey towards an agentic future and how we empower users to build AI Agents that are smarter, more adaptable, and ready for the future.
A no-code platform for building LLM apps
SpellVault was founded with a clear mission: to democratize access to AI for everyone at Grab, regardless of their technical expertise. Initially launched as a no-code LLM app builder, the platform was built on a foundation of RAG pipelines and basic plugin support.
Early on, we recognized that the true potential of AI apps extends beyond the capabilities of language models alone. Their real value lies in the ability to seamlessly interact with external systems and diverse data sources. This insight drove our commitment to minimizing barriers and ensuring users could access data from various sources with ease. From the very beginning, we centered our efforts on three key focus areas:
Comprehensive RAG solution with useful integrations
From the start, the SpellVault team prioritized enabling users to enhance their LLM apps with data through RAG. Rather than solely relying on the LLM’s internal information, we wanted the apps to ground their responses in up-to-date, contextually relevant, and factual information. SpellVault has built-in integrations with knowledge sources such as Wikis, Google Docs, as well as plain text and PDF uploads. These capabilities empower users to build assistants that reference relevant knowledge and provide more accurate, verifiable answers.
Plugins to fetch information on demand
To move beyond static knowledge retrieval, we needed a way for apps to act dynamically. This was made possible through SpellVault plugins—modular components that allow apps to interact with internal systems (e.g. service dashboards, incident trackers) and external APIs (e.g. search engines, weather data). Rather than being confined to their initial prompt and data, these plugins can fetch fresh information at runtime. From the available plugin types, users can create their own instances of plugins with custom settings, enabling highly specialized functionality tailored to their specific workflows. For instance, with SpellVault’s HTTP plugin, users can define custom endpoints and credentials, enabling their AI apps to make tailored HTTP calls during runtime. These custom plugins have become the backbone of many of our most impactful apps, empowering teams to seamlessly integrate SpellVault with their existing systems and processes.
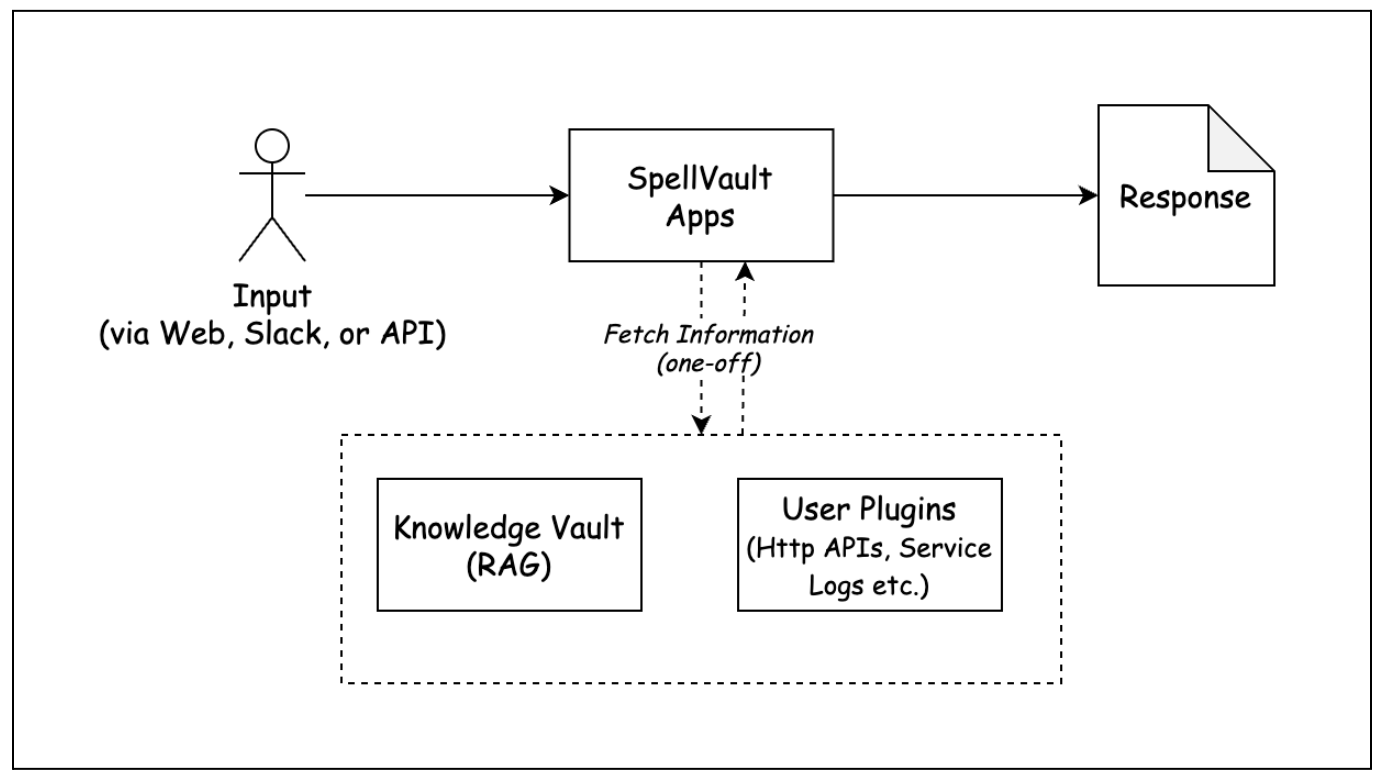
Making SpellVault accessible via common interfaces: Web, Slack, API
One of our primary goals was to make AI seamlessly accessible and useful within the tools users already use—whether it’s a browser or Slack. With SpellVault, users can make their AI apps in minutes and start using them via browser or Slack messaging immediately and intuitively, without requiring any additional setup. We also exposed APIs that enabled other internal services to integrate with SpellVault apps for a variety of use cases. This multi-channel approach ensured that SpellVault wasn’t just a standalone sandbox but a platform woven into existing tools and processes.
Users quickly adopted the platform, creating thousands of apps for internal productivity gains, automation, and even production use cases. The platform’s success validated our hypothesis that there was significant demand for democratized AI tools within the organization.
Evolution over time
The AI landscape over the past few years has been defined by relentless change. New frameworks, execution paradigms, and standards have emerged in quick succession, each promising to make AI systems more powerful, more reliable, or more extensible. At Grab, we recognized that for SpellVault to stay relevant, it could not remain static. It needed to evolve in tandem with the ever-changing ecosystem, continuously incorporating valuable advancements while ensuring a seamless experience for our users.
This philosophy of continuous adaptation has guided SpellVault’s journey. From its early days as a simple RAG-powered app builder with a few plugins, the platform grew to support an extensive number of plugin types, richer execution models, and eventually a unified approach to tools. Each step was a response both to the needs of our users and to the shifting definition of what “building with AI” meant in practice. Rather than opting for a complete overhaul, SpellVault has embraced incremental advancements, ensuring that users can seamlessly benefit from new capabilities without disruption.
This approach to evolution has naturally positioned SpellVault to transition from a platform for LLM apps to one designed for AI agents. The following section delves into this transition in greater detail.
Expanding capabilities
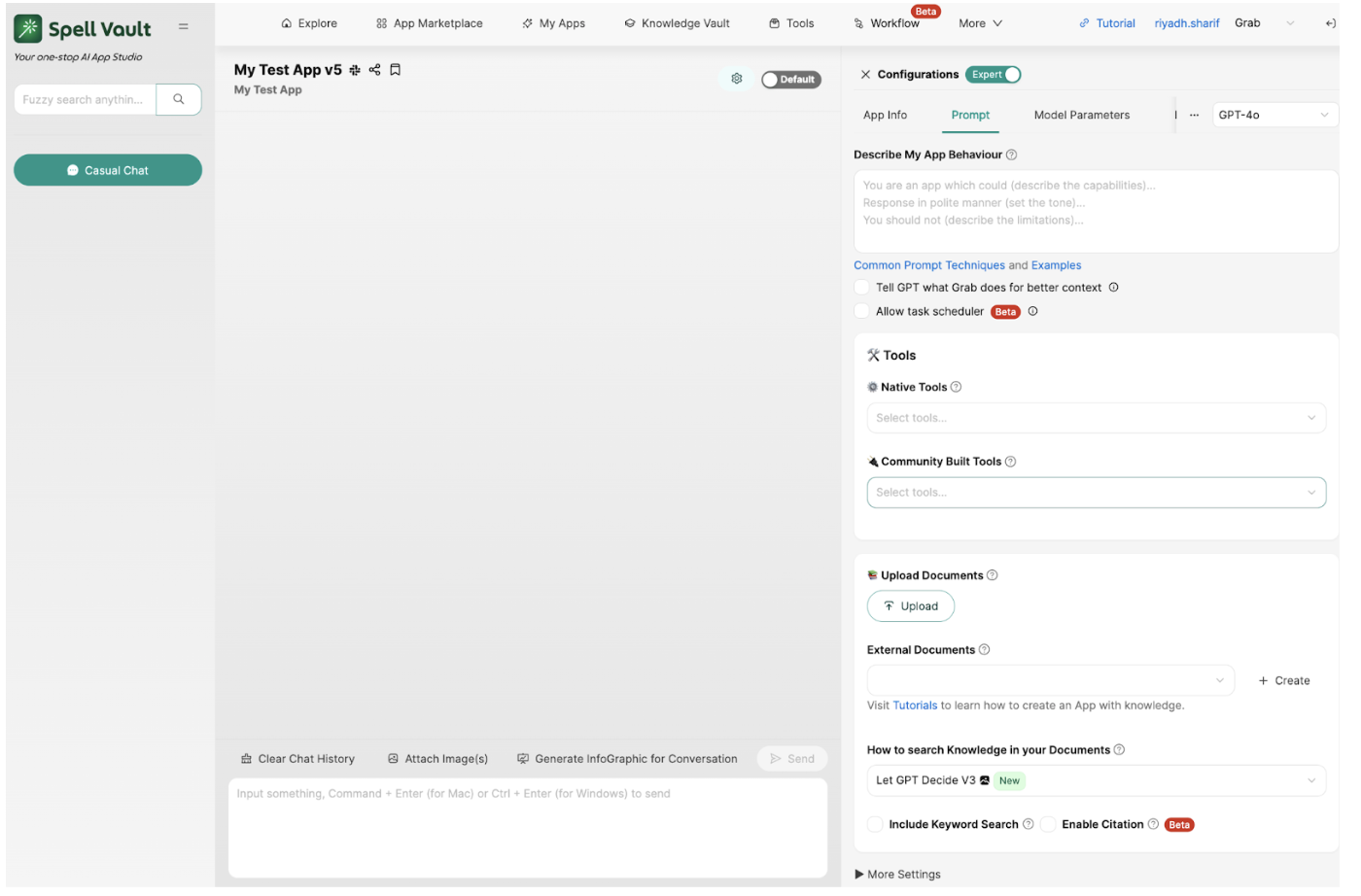
Over time, we introduced numerous new capabilities to SpellVault, driven both by user feedback and our commitment to innovation and staying ahead of industry trends. For instance, we extended support for different plugin types, enabling integrations with tools like Slack and Kibana, and continuously added more integrations to enhance the platform’s versatility. We implemented auto-updates for users’ Knowledge Vaults, ensuring their data remained current. With more users building with the platform, ensuring the trustworthiness of responses generated by SpellVault apps became increasingly important. We included citation capability to mitigate some of that concern. Recognizing the need for more precise answers to mathematical problems, we developed a feature that enabled LLMs to solve such problems using Python runtime. Additionally, many users requested an automated way to trigger their LLM apps, which led to the creation of a Task Scheduler feature that allows LLMs to schedule actions based on natural language user input.
A significant milestone in SpellVault’s evolution was the introduction of “Workflow,” a drag-and-drop interface within the platform that empowered users to design deterministic workflows. These workflows enabled users to seamlessly combine various components from the SpellVault ecosystem—such as LLM calls, Python code execution, and Knowledge Vault lookups—in a predefined and structured manner. This enabled advanced use cases for many users.
Shifting the execution model
As SpellVault evolved, a fundamental shift took place in the way its apps were executed internally. We transitioned from our legacy executor system, which facilitated one-off information retrieval from the Knowledge Vault or user plugins, to a more advanced graph based executor. This empowered SpellVault’s app execution with nodes, edges, and states that supported branching, looping, and modularity. This laid the groundwork for more sophisticated agent behaviors, moving beyond the linear input-output paradigm.
This transformed all existing SpellVault apps into ‘Reasoning and Acting’ agents, better known as ReAct agents - a “one size fits many” solution that significantly enhanced the capabilities of these apps. By enabling them to leverage the Knowledge Vault and plugins in a more agentic and dynamic manner, the ReAct agent framework allowed apps to perform more complex tasks while seamlessly preserving their existing functionality, ensuring no disruption to their behavior.
In addition, the internal decoupling of the executor and prompt engineering components enabled us to design multiple execution pathways with ease. This allowed us to provide generic Deep Research capability to any SpellVault app via a simple UI checkbox, as well as sophisticated internal workflows that cater to high-ROI complex use cases like on-call alert analysis. The Deep Research capability came with SpellVault’s ability to search across internal information repositories (e.g., Slack messages, Wiki, Jira) within Grab, as well as searching online for relevant information.

Towards an agentic framework
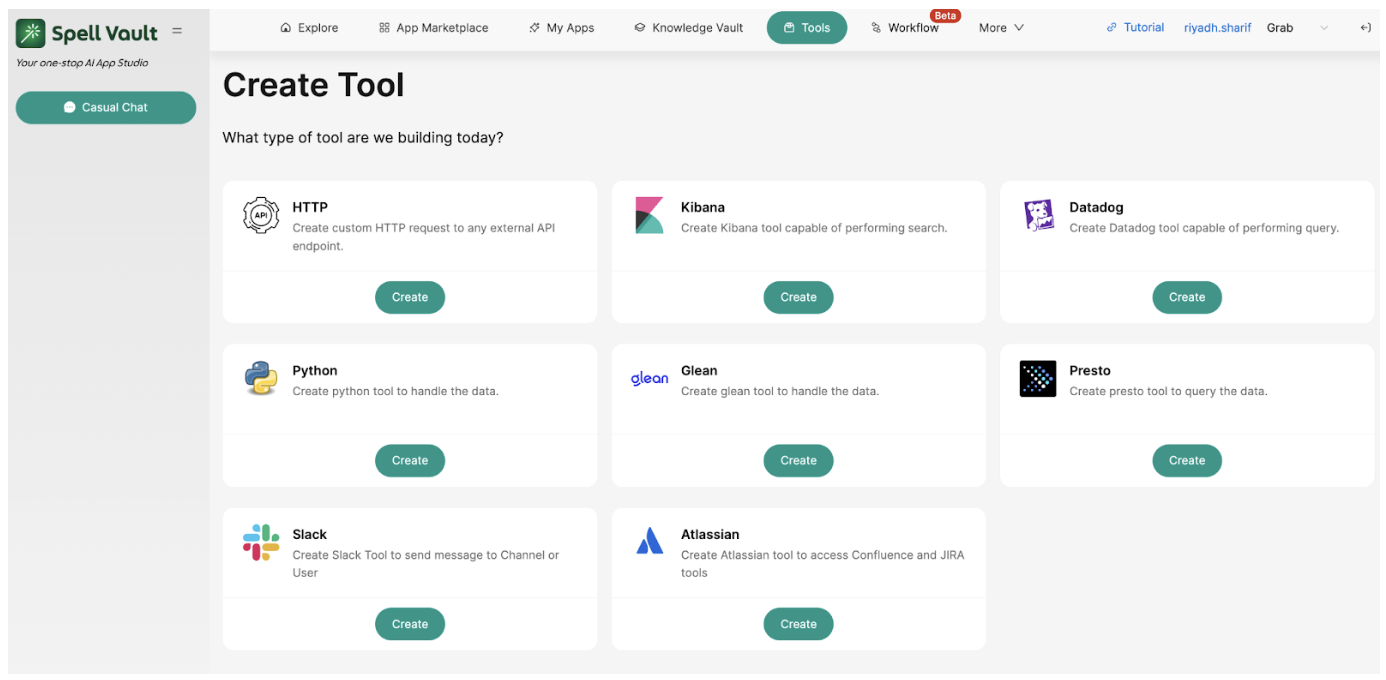
Over time, several capabilities were added to SpellVault, including features like Python code execution and internal repository search. Initially, these functionalities were integrated directly into the core PromptBuilder class. For users, these features were primarily accessible through simple checkboxes in the user interface. As SpellVault gradually transitioned towards giving more agency to user-crafted apps, we recognized that these capabilities should instead be positioned as “Tools” for LLMs to use with greater autonomy, similar to how ReAct agent–backed apps have been using SpellVault’s user plugins. We also understood that this shift could bring a clearer mental model for users where they were no longer simply toggling features but creating AI agents with access to a defined set of tools. The agents could then decide when and how to use those tools intelligently to accomplish tasks, making the overall experience more natural and intuitive.
This recognition led to the consolidation of these scattered capabilities into a unified framework called “Native Tools.” These Native Tools, along with SpellVault’s existing user plugins—rebranded as “Community Built Tools”—formed a comprehensive collection of tools that LLMs could dynamically invoke at runtime. Despite being grouped under the same umbrella, a key distinction was maintained: Native Tools required no user-specific configuration (e.g., performing internet searches), whereas Community Built Tools were custom, user-configured entities (e.g., invoking specific HTTP endpoints) created from available plugin types, often requiring credentials or other personalized settings.
This consolidation of capabilities under a unified Tools abstraction and enabling SpellVault apps to invoke them with greater autonomy marked a pivotal milestone in the platform’s evolution. It meaningfully shifted SpellVault toward making agentic behavior more natural, discoverable, and extensible for every app.

SpellVault as an MCP service
As we streamlined SpellVault’s internal capabilities into a unified tools framework, we also turned our focus outward to align with industry standards. The growing adoption of the Model Context Protocol (MCP) presented an opportunity for agents and clients to seamlessly interact without requiring custom integrations. To remain at the forefront of innovation, we adapted SpellVault to function as an MCP service, enabling it to actively participate in this evolving ecosystem. This extension brought two key advancements:
-
SpellVault apps as MCP tools: Each app created in SpellVault can now be exposed through the MCP protocol. This allows other agents or MCP-compatible clients, such as IDEs or external orchestration frameworks, to treat a SpellVault app as a callable tool. Instead of living only inside our web user interface or Slack interface, these apps become accessible building blocks that other systems can invoke dynamically.
-
RAG as an MCP tool: We extended the same idea to our Knowledge Vaults. Through MCP, external clients can search, retrieve, and even add information to Vaults. This effectively turns SpellVault’s RAG pipeline into an MCP-native service, making contextual grounding available to agents beyond SpellVault itself.
While building the SpellVault MCP Server, we also created TinyMCP - a lightweight open-source Python library that adds MCP capabilities to an existing FastAPI app as just another router, instead of mounting a separate app.
By exposing both apps and RAG through MCP, we shifted SpellVault from being a self-contained platform to becoming an interoperable service provider in the agentic ecosystem. Users still benefit from the no-code simplicity inside SpellVault. However, the output of their work, apps, and knowledge, are now usable by other agents and tools outside of it.
Conclusion
SpellVault’s evolution shows how a platform can adapt with the AI landscape while staying true to its original mission of making powerful technology accessible to everyone. What began as a no-code builder for LLM apps has steadily expanded into an agentic platform - one where apps can act with more intelligence, agency, and context and interact with the systems around them.
This progress wasn’t the result of a single breakthrough, but of steady, incremental improvements that introduced new capabilities while preserving ease of use. By layering in these advancements thoughtfully but boldly, SpellVault has managed to support more sophisticated agentic behaviors without compromising its original goal of democratizing AI at Grab.
Join us
Grab is a leading superapp in Southeast Asia, operating across the deliveries, mobility and digital financial services sectors. Serving over 800 cities in eight Southeast Asian countries, Grab enables millions of people everyday to order food or groceries, send packages, hail a ride or taxi, pay for online purchases or access services such as lending and insurance, all through a single app. Grab was founded in 2012 with the mission to drive Southeast Asia forward by creating economic empowerment for everyone. Grab strives to serve a triple bottom line – we aim to simultaneously deliver financial performance for our shareholders and have a positive social impact, which includes economic empowerment for millions of people in the region, while mitigating our environmental footprint.
Powered by technology and driven by heart, our mission is to drive Southeast Asia forward by creating economic empowerment for everyone. If this mission speaks to you, join our team today!